How a Deposit Jelly Machine Can Improve Your Candy Production (Practical Guide for Manufacturers)
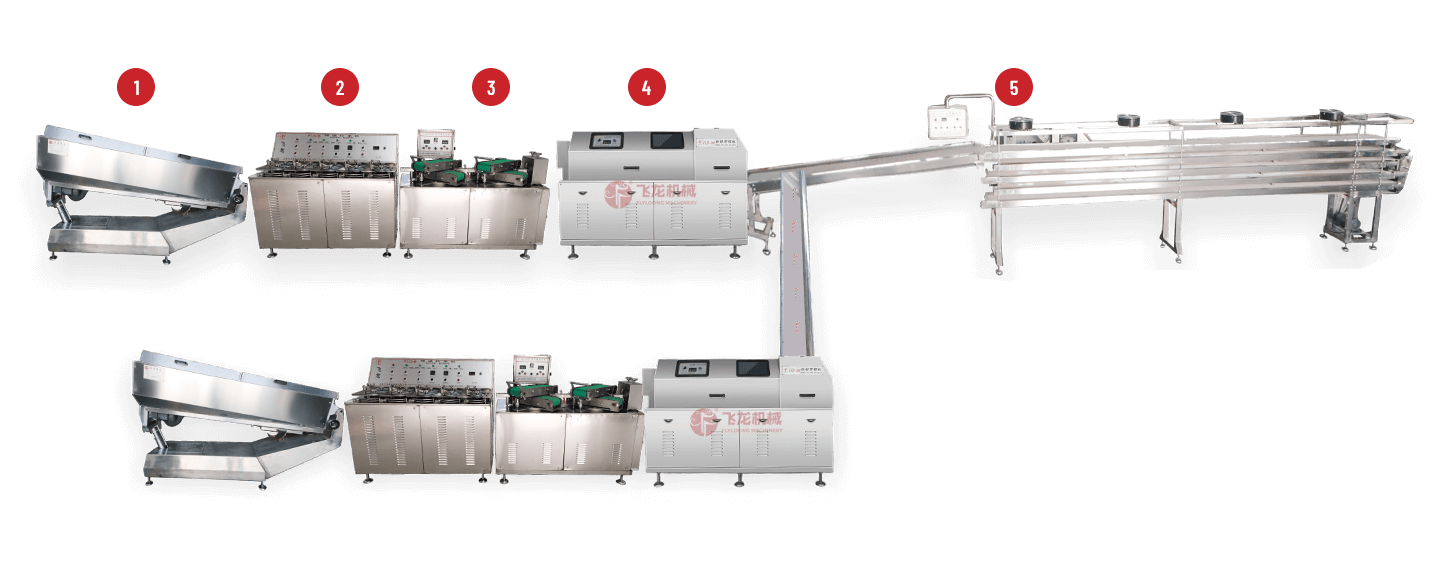
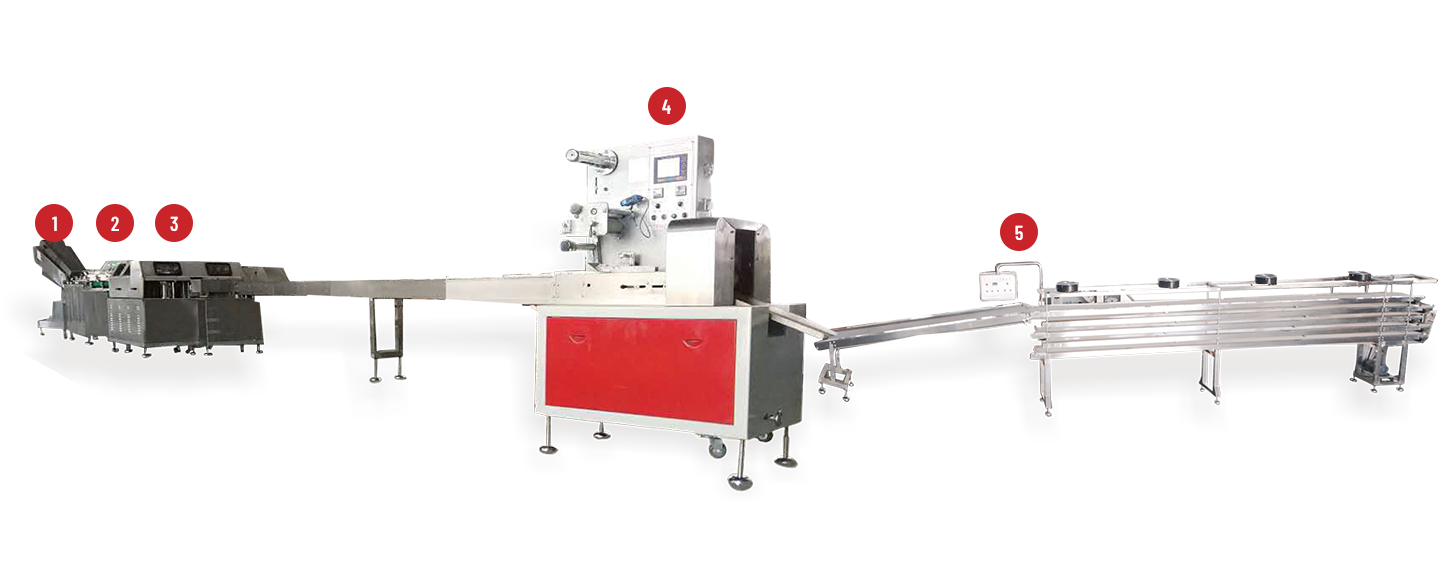
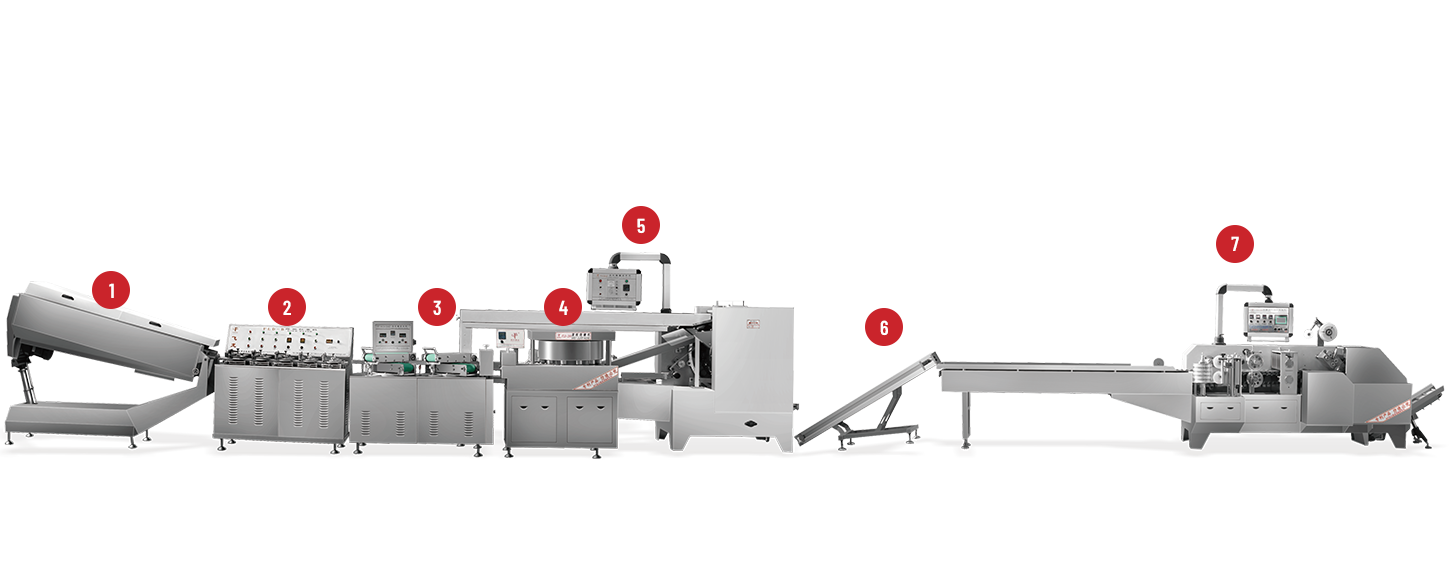
A Deposit Jelly Machine is central to many confectionery lines that make jelly sweets, gummy centers, filled candies, and similar products. Placed between cooking/kettle processes and downstream finishing — sugar-coating, cooling, or enrobing — the machine deposits precise portions of gel or jelly into molds, onto carriers, or into shells. When selected and set up correctly, it raises throughput, stabilises product weight, and reduces manual handling — all of which matter to a factory's bottom line and product consistency.
This guide is written for production managers, engineers, and procurement teams. It focuses on real-world choices: features that affect output, safe ways to increase speed without sacrificing quality, the settings that influence texture and consistency, maintenance practices that keep lines running, and practical adjustments to handle different candy types. A compact comparison table is included so you can judge options at a glance.
Why deposit systems matter for gummy and jelly production
A deposit system does more than place dollops of jelly. It directly influences:
- Portion accuracy and weight control — consistent portions reduce giveaway and regulatory headaches.
- Texture and mouthfeel — deposition pressure, nozzle design, and timing change how the gel sets and, ultimately, how it feels when eaten.
- Production speed — precise dosing minimizes pauses, so upstream processes (cooking/tempering) run smoothly.
- Hygiene and traceability — modern machines improve cleaning and batch tracking, which support food safety systems.
When deposition is inconsistent, consequences show up downstream: uneven cooling, variable coating adhesion, or more rejects. A reliable deposit process reduces rework and helps maintain predictable ingredient usage.
Core features to prioritise when evaluating machines
Not all depositors are the same. Focus on features that influence accuracy, uptime, and flexibility.
Accurate dosing mechanism
Check whether the machine uses positive displacement pumps, piston depositors, or time/pressure dosing. Positive displacement and piston systems typically deliver more repeatable doses across a range of viscosities.
Nozzle and tooling variety
Interchangeable nozzles and mould plates let the same machine handle multiple shapes and sizes. Look for quick-change tooling to speed SKU changeover.
Temperature and viscosity control
Jelly consistency depends on temperature and shear history. Machines with local heating/cooling and active viscosity compensation make it easier to run long, steady batches.
Gentle handling options
Soft or shear-sensitive centers require gentle filling. Machines that offer low-shear pumping modes, slow-start dosing, or dampened stroke settings preserve texture and avoid air entrapment.
Integrated cleaning and hygiene features
Hygienic design (rounded corners, drainable zones, CIP-compatible piping) and easy disassembly reduce cleaning time and contamination risk.
Recipe memory and controls
PLC-based recipe storage for temperature, dosing volume, and timing simplifies shift handovers and reduces operator variability.
Modular layout and footprint
In small plants, footprint matters. Modular machines that grow with your line let you start modestly and add features — extra heads, chill plates, or in-line lidders — later.
Fault logging and diagnostics
Machines that log errors and provide clear fault messages shorten troubleshooting time and reduce unscheduled downtime.
How depositors improve production efficiency — practical pathways
A deposit system improves efficiency in several linked ways:
- Direct weight control: Accurate dosing reduces the need for downstream weight checks and trimming.
- Fewer manual steps: Automated deposition replaces hand-filling or spooning operations, freeing labour for higher-value tasks.
- Smoother flow: When upstream and downstream speeds match, the whole line runs with fewer stops and starts, reducing thermal cycling in cooking kettles.
- Reduced scrap: Repeatable dosing and clean nozzle operation reduce spills, stringing, or sticky rejects.
- Faster changeovers: Quick-change mould plates and stored recipes make SKU swaps less costly in minutes of lost production.
A conservative factory often gains measurable throughput by removing small bottlenecks in deposition alone — a 5–15% output improvement is common as manual variability disappears.
Which machine settings influence jelly texture and consistency
Several depositor parameters directly affect product texture. When operators know which knobs matter most, they get to consistent results faster.
Deposit volume and speed
The basic volume per deposit sets the portion size. But speed interacts: fast deposits at high pressure can shear gels and change texture. Slower deposits often yield rounder, smoother portions for delicate recipes.
Nozzle diameter and geometry
Nozzles control flow pattern. Narrow, long nozzles may cause stringing with sticky gels; wider, short nozzles can reduce surface defects. For molded pieces, nozzles that produce a gentle, laminar fall fill cavities without entraining air.
Dwell and settle time
Some gels need time in the mould before the next operation (cooling or demoulding). The machine's cycle timing should allow the gel to settle and prevent surface pitting.
Head temperature and product feed temperature
Warm product flows easier; too warm and it may absorb air or over-spread. Consistent feed temperature ensures repeatable viscosity and dosing.
Pump type and stroke control
Smooth stroke control avoids pressure spikes. Use pumps with dampened stroke transitions or electronically controlled pistons for fragile gels.
Document SKU-specific recipes for all these settings; treat them as the baseline for future runs.
A quick comparison table: nozzle types, pump choices, and recommended uses
| Component | Typical options | Practical advantage | Recommended for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pumping | Piston, peristaltic, gear, time/pressure | Piston = precise, peristaltic = hygienic, gear = high flow | Piston for dosing gels; peristaltic for fibre/particles |
| Nozzle | Short wide, long narrow, tapered, multi-lumen | Wide = low stringing; long = controlled flow | Wide short for sticky gels, tapered for shaped fills |
| Dosing control | Electronic stroke, timed pressure, servo | Servo = repeatability | High-mix lines needing fast SKU changes |
| Heating | Inline heater, jacketed reservoir | Local control of viscosity | Recipes sensitive to ±1–2°C |
| Cleaning | Manual disassembly, CIP-capable | CIP reduces downtime and contamination risk | High hygiene, frequent flavour changes |
Safe ways to increase throughput without sacrificing quality
Speed is tempting, but pushing settings blindly produces defects. Follow these safe, iterative steps to raise throughput:
- Stabilise baseline: Run a stable batch at nominal speed and log key metrics — weight variance, sealability, surface finish.
- Increase in small steps: Raise conveyor or dosing rate by 5–10% and re-check metrics.
- Watch temperature: Faster cycles may cool product less; ensure reservoir and feed temperatures are maintained.
- Monitor stringing and entrainment: Faster deposition often increases stringing; adjust nozzle type or re-tune pump stroke.
- Maintain settle time: If products need a pause to level, add short dwell conveyors or slow zones rather than pushing cooling speed.
- Record every change: Keep recipe changes logged to allow rollback.
Small, controlled steps make speed improvements sustainable and safe.
Maintenance routine that keeps deposit lines productive
A regular maintenance regimen prevents surprises and preserves quality.
Daily (end of shift)
- Remove product residue from nozzles and feed pipes.
- Wipe machine surfaces and inspect seals.
- Check dosing repeatability on a 10-piece sample.
Weekly
- Strip nozzle assemblies for cleaning and inspect for wear.
- Check pump seals, hoses, and check valves.
- Verify temperature probe calibrations.
Monthly
- Review fault logs and address recurring alarms.
- Inspect gearbox and drive belts for wear.
- Replace soft seals if operating in abrasive or high-temperature conditions.
Quarterly (or per manufacturer hours)
- Full CIP cycle (if available) and inspection of internal piping.
- Overhaul of essential pumps and serviceable components.
- Verification of PLC backup and recipe integrity.
Document all steps. A simple digital log (even a shared spreadsheet) helps correlate maintenance actions with production trends.
Adjustments for different candy types — practical examples
Different centres need different approaches. Here are common cases and recommended deposition strategies.
Soft, high-moisture jelly (e.g., fruit jellies)
- Use low-shear piston dosing.
- Short, wide nozzles reduce stringing.
- Maintain feed temperature to avoid premature setting.
- Allow longer settle time in moulds before transfer.
Chewy centres with inclusions (nut pieces, fruit bits)
- Consider peristaltic or large-bore piston pumps tolerant of particulates.
- Use nozzles with larger lumen or multi-lumen feed heads.
- Slow down feed speed slightly to avoid clogging.
Gel-filled chocolates or enrobed centres
- Precisely timed dosing so chocolate shell formation synchronises with filling.
- Use gentle deposits to avoid shell rupture.
- Coordinate cooling tunnel temperature to stabilise shells post-filling.
Sugar-coated, small-portion sweets
- High repeatability and small-volume dosing are critical.
- Servo-driven micro-dose systems produce consistent weight and minimise giveaway.
These are starting points — run short trials to verify behaviour with your exact formulations.
Hygiene, traceability, and regulatory compliance
Depositors touch food directly; design and process must support regulations (HACCP, FSMA, or local standards).
- Hygienic design: smooth, drainable surfaces, no dead zones, easy access for cleaning.
- Batch traceability: link deposit times and recipes to batch IDs so any issue is traceable back to deposits.
- CIP capability: where feasible, CIP piping reduces manual cleaning and contamination risk.
- Material certifications: contact surfaces should have food-grade approvals (stainless steel grades, FDA-compliant seals).
- Operator hygiene: ensure PPE, hand-wash stations, and clean-room practices where required.
Traceability data (time-stamped logs of recipes, operator IDs, and batch numbers) not only helps recalls but improves continuous process improvement.
Troubleshooting checklist: quick fixes for common issues
When defects occur, follow a short diagnostic path:
Problem: Underfill or overfill
- Check pump calibration and stroke length.
- Verify supply viscosity and temperature.
- Inspect nozzle blockage or wear.
Problem: Stringing or tails on deposits
- Reduce deposit pressure or slow nozzle retract.
- Switch to a wider nozzle or adjust nozzle geometry.
- Increase feed temperature slightly if product is too viscous.
Problem: Air pockets or voids
- Look for air ingress in suction lines and degas reservoirs.
- Verify pump priming and check valves for leaks.
Problem: Inconsistent weights across a shift
- Check for temperature drift, especially in start-to-shift warm-up period.
- Verify belt slippage or encoder miscounts on the timing system.
A short printed flowchart near the machine with these checks saves valuable minutes on-shift.
Cost control: reducing ingredient giveaway and scrap
Ingredient giveaway is real cost. Tactics that help:
- Calibrate dose to target weight and tighten tolerance gradually.
- Use in-line checkweighers and automatic reject systems to catch outliers before packing.
- Track film, sugar, or coating acceptance tolerances — consistent deposit mass reduces downstream variation and trimming.
- Capture trim or overflow where food safety permits, and reintegrate via controlled rework loops.
Measure giveaway per 1,000 units and set monthly targets. Small percentage improvements compound into meaningful savings.
Procurement and acceptance: how to evaluate suppliers
When you evaluate machines, structure trials and contractual acceptance carefully.
- On-site trials: insist suppliers trial with your product and film. Lab tests are useful; site tests are decisive.
- Acceptance criteria: define acceptable weight variance, speed, and defect rate before purchase. Put them in the purchase order.
- Spare parts and training: include a spare-parts kit and operator training in the contract.
- Warranty and SLAs: clarify warranty scope and response times for critical failures.
- Reference checks: visit a similar facility using the same model to observe long-term behaviour.
A well-specified acceptance stage avoids disagreements later and ensures the machine meets your production reality.
Simple ROI framework for decision-makers
A quick matrix helps prioritise capital allocation:
- Measure current manual labour cost for equivalent wrapping/filling tasks.
- Estimate film and ingredient giveaway under current process.
- Estimate scrap and rework losses per month.
- Get vendor estimates for machine cost, expected energy use, and consumable costs.
- Calculate monthly savings (labour + giveaway reduction + rework avoided) and divide capital cost by monthly net savings to get payback months.
Use conservative savings assumptions. Pilots often shorten payback by confirming assumptions.
Practical start-up checklist for runs
When commissioning a depositor for time, follow this checklist:
- Confirm feed temperature and viscosity are in target range.
- Load correct nozzle and tighten all fittings.
- Run an initial warm-up purge and stabilise temperatures.
- Run a 30-piece qualification sample and weigh each piece.
- Check surface finish and demoulding behaviour.
- Record the recipe into the PLC and lock for operator use.
- Schedule a review after full production shift to note small adjustments.
This checklist captures the crucial early steps that determine long-term stability.
Combine equipment, recipes, and people
A deposit jelly system gives measurable benefits when it is evaluated and integrated as a process node, not merely as a piece of kit. Success depends on matching pump and nozzle technology to your formulation, documenting recipes, training operators, and running a realistic maintenance plan. Small, consistent improvements to deposit repeatability and cleaning time translate into lower waste, better quality, and a smoother shift.

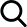
 ENG
ENG
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى






 +86-(0)515-8465666
+86-(0)515-8465666 +86-(0)515-85566996
+86-(0)515-85566996 +86-138 1559 9708
+86-138 1559 9708 flyloong@flyloongcn.com
flyloong@flyloongcn.com 
 Home
Home